| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
Tags
- install
- pycharm
- imread
- LSTM
- E-P1
- GitHub
- synology
- javascript
- pandas
- keras
- pip
- dataframe
- Python
- GT-S80
- DFS
- CNN
- index
- mean
- Button
- Lotto
- 삼성소프트웨어멤버십
- mariadb
- SciPy
- Series
- ipad
- SPL
- Splunk
- RNN
- Numpy
- 알고리즘
Archives
- Today
- Total
잠토의 잠망경
[ML] Multiple Input Series - Multivariate CNN Models 본문
GITHUB
https://github.com/yiwonjae/Project_Lotto/blob/master/Book_001/p096.py
0. 목표
data가 두가지 종류가 있다.
현재 포함 과거 data 총 3단계를 바탕으로 예측되는 data를 산출한다.
input data
10, 15
20, 25
30, 35
prediction data
651. DATA
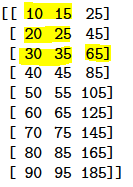
in_seq1 = np.asarray([10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90])
in_seq2 = np.asarray([15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 65, 75, 85, 95])
out_seq = np.asarray([in_seq1[i]+in_seq2[i] for i in range(len(in_seq1))])
in_seq1 = in_seq1.reshape((in_seq1.shape[0], 1))
in_seq2 = in_seq2.reshape((in_seq2.shape[0], 1))
out_seq = out_seq.reshape((out_seq.shape[0], 1))
dataset = np.hstack((in_seq1, in_seq2, out_seq))가상의 data를 만드는 것으로 특별한 의미가 있는건 아니다.
개념을 설명하기 위한 장치이다.
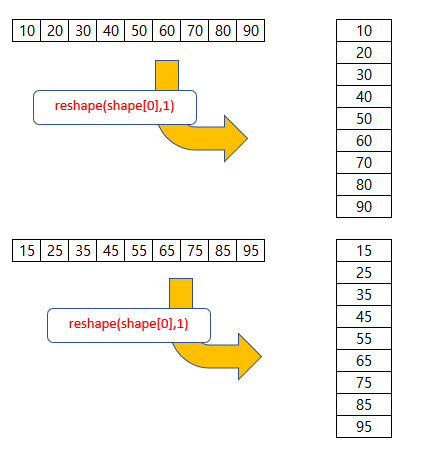
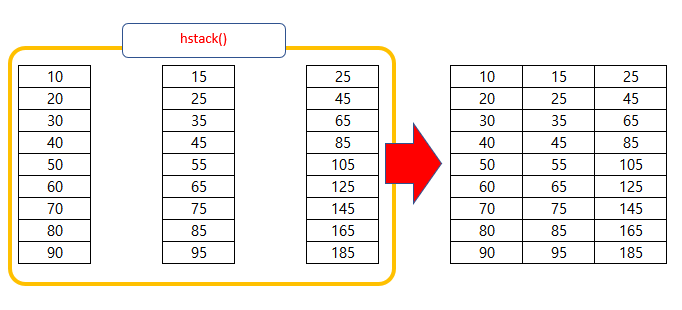
2. DATA 정제
X
from numpy import ndarray
import numpy as np
def split_sequence(sequence:list, n_steps)->(ndarray, ndarray):
x, y = [], []
for i in range(len(sequence)):
if(i+n_steps>len(sequence)):
break
x.append(sequence[i:i+n_steps, 0:2])
y.append(sequence[i+n_steps-1, -1])
return (np.asarray(x), np.asarray(y))
n_steps = 3
(x, y) = split_sequence(dataset, n_steps)
n_feature = x.shape[2] # 종류
Y
3. 학습
from keras import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Conv1D, MaxPool1D, Flatten
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv1D(64, 2, activation='relu', input_shape=(n_steps, n_feature))) #multivariate
model.add(MaxPool1D())
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(50, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
model.fit(x, y, epochs=2000, verbose=1)
4. 표시
x_input = np.asarray([[80,85],[90,95],[100, 105]]) # 205 나올 것으로 예측
x_input = x_input.reshape((1, n_steps, n_feature))
yhat = model.predict(x_input)
print(yhat) #[[206.04001]]
Comments



